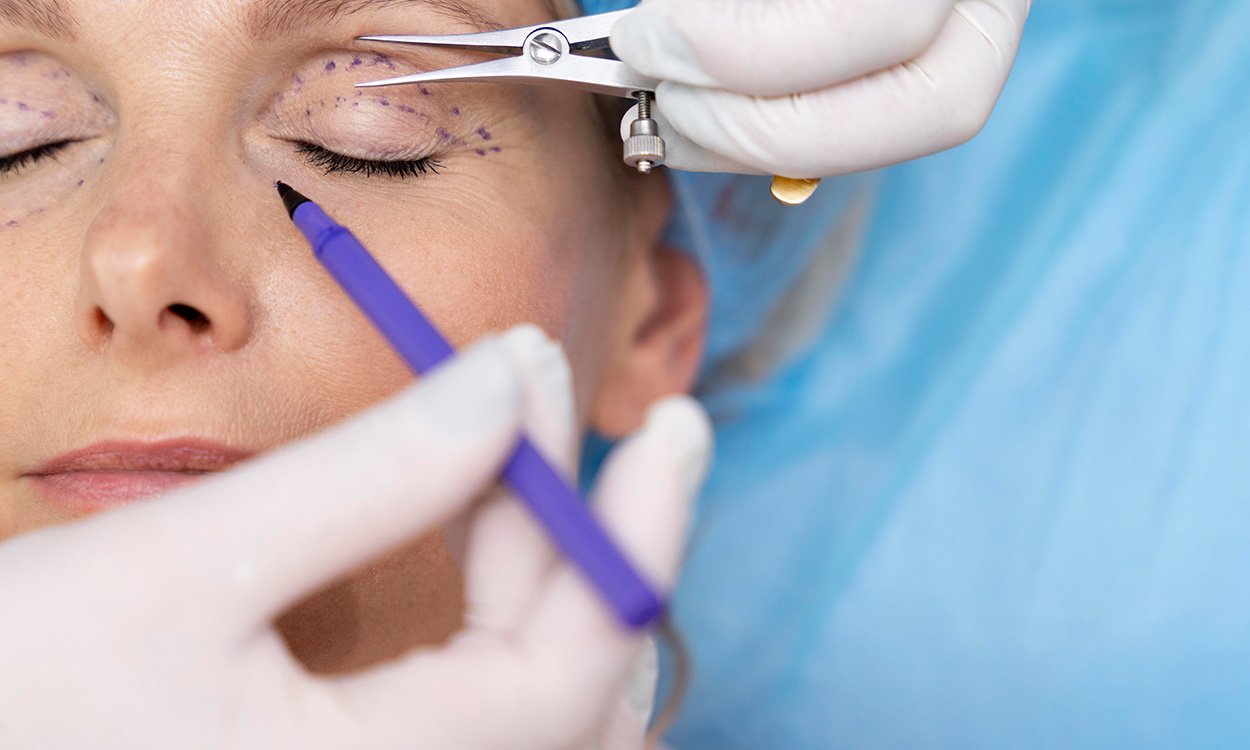
The eye area is often the most captivating part of the face that others notice first. The first signs of facial aging typically appear in this area (1). The desire for a younger and fresher facial appearance is the primary reason why people seek clinical solutions through surgical or non-surgical methods, and this demand has been increasing in both male and female patients in recent years.
Blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery), performed for both cosmetic and functional purposes, is one of the most common surgeries worldwide (2). Blepharoplasty is the surgical repair of the upper and lower eyelids, either individually or both, depending on the patient’s needs. These procedures can be performed to eliminate signs of aging around the eyes or to correct an unaesthetic appearance. The surgery typically involves a surgical procedure in which excess eyelid skin, orbicularis oculi muscle, and orbital fat are removed and reshaped (3). Eyelid surgery was first defined as blepharoplasty by an ophthalmologist, Karl Ferdinand Von Graefe, in 1818 (4).
Understanding the anatomy of the upper eyelid is essential for upper eyelid surgeries. The thinnest skin in the body and the absence of a subcutaneous fat layer distinguish this area from other structures (5). Evaluating the brow position and planning the surgery accordingly is important for achieving beautiful and functional results. The muscle groups that control the eyebrows are among the most important muscles of facial expression and are strong indicators of mood (6). Correcting brow ptosis during upper eyelid surgery can also lead to significant results.
Upper eyelid problems can lead to consequences such as an aged appearance, dull appearance, cosmetic concerns, chronic blepharitis, dry eye, and irritation in the eye due to misdirected eyelashes. Upper eyelid surgeries are performed for cosmetic reasons, dermatochalasis (drooping of the eyelids), eyelid drooping that obstructs the visual field, tumors, trauma, and similar conditions (7). Lower eyelid surgeries aim to reshape the aging lower eyelids. It is a surgical procedure involving the reshaping of excess skin and fat tissue through transcutaneous and transconjunctival surgical techniques (8). Before surgery, the patient should undergo a complete and detailed eye examination, and a general medical and eye history should be taken. Preoperative photographs should be taken in a neutral position. Visual acuity, upper eyelid position, eyelid crease, crease distance, brow position, the effect of the forehead on the eyelid, and tear film examination should be performed in detail. Marking is done according to the surgical plan made before the surgery, and then the surgical procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia after providing sterile conditions (9).
After surgery, it is recommended that the patient avoid lifting heavy loads, exposure to direct sunlight, and wearing makeup. Postoperative eye examinations, ice application, and the use of sunscreen are important to prevent corneal dryness (9).
1. De Biasio F, Miotti G, Zingaretti N, Castriotta L, Parodi PC. Study on the Aging Dynamics of the Periorbital Region: From Observation to Knowledge of Physiopathology. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;35:333–341.
2. Baroni A. Non-surgical blepharoplasty with the novel plasma radiofrequency ablation technology. Skin Res Technol. 2020;26:121–124.
3. Rebowe RE, Runyan C. Blepharoplasty. 2022 Jul 25. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan
4. Von Graefe CF. De Rhinoplastice. Berlin: Dietrich Reimer; 1818. p. 13
5. Kersten RC, Codere F, Dailey RA. Orbit, Eye-lids, and Lacrimal System. San Francisco: American Academy of Ophthalmology; 2003
6. Nerad JA. Oculoplastic Surgery: The Requisites in Ophthalmology. St. Louis: Mosby; 2001.
7. Leather BB, editor. Oculoplastic Surgery. London, UK: Informa Healthcare; 2011. Blepharoplasty; pp. 310–45.
8. Bhattacharjee K, Ghosh S, Ugradar S, Azhdam AM. Lower eyelid blepharoplasty: An overview. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 Oct;68(10):2075-2083. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2265_19. PMID: 32971612; PMCID: PMC7727946.
9. Bhattacharjee K, Misra DK, Deori N. Updates on upper eyelid blepharoplasty. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017 Jul;65(7):551-558. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_540_17. PMID: 28724810; PMCID: PMC5549405.